Every day, we hear about disruption in the mainstream media. However, just a few people understand what it implies or how to make it. We now live in a world of limitless options and opportunities, with new products and services being introduced at an ever-increasing rate. In the era of innovation, new solutions can be produced quicker than ever before on top of current technology. This indicates that there will be a new, even larger wave of invention ahead of us, and practically every industry will be influenced in some manner.
Approximately half of the S&P Fortune 500 companies are expected to be replaced by disruption within the next decade. As a result, it is critical for businesses to not pass up opportunities to adapt.
Understanding what disruptive innovation is all about is the first step in creating it. A concept, product, or service that disrupts an existing market or establishes an entirely new market sector is referred to as disruptive innovation.
Disruption occurs in practice when typical value drivers in an existing market are dramatically altered. Typically, a new entrant enters an established market with new technology or a new business strategy, bringing fresh value that differentiates from the incumbent's offers.
In the innovation matrix, disruptive innovation is one of four categories of inventions.
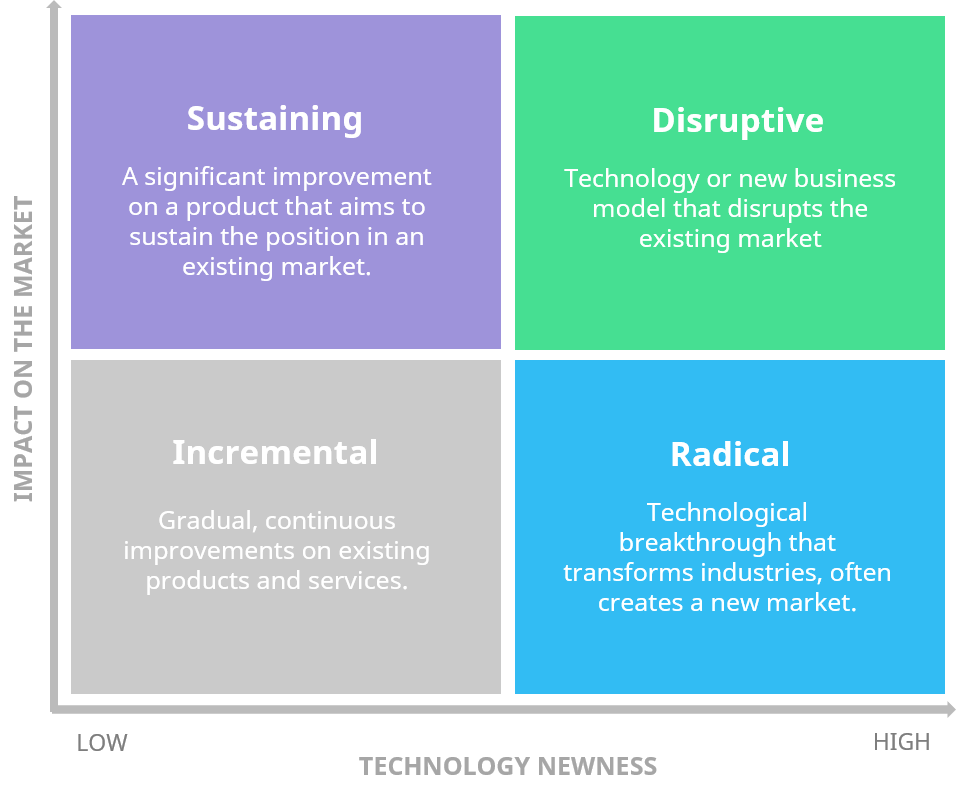
Incremental innovation is the process of continuously improving current products or services in order to add value to a market that already exists. With features including product line extensions, cost reductions, and next-generation products, it focuses on minimizing flaws and incrementally enhancing performance. This form of invention is short-term in nature, with little technological advancement and little market influence. BMW's next-generation 3 series, for example, and Gillette's new razor.
Taking the lessons, skills, and general technology learned in one market and applying them to a different industry is known as architectural innovation. As long as the new market is receptive, this invention is fantastic at attracting new customers. Because of the reliance on and reintroduction of proven technology, the risk of architectural innovation is usually low.
Most of the time, it will need to be tweaked to meet the needs of the new market. NASA's Ames Research Center tried to increase the safety of aeroplane cushions in 1966. They were successful by inventing a new sort of foam that reacts to pressure yet miraculously returns to its previous shape.
It was first commercially sold as medical table pads and sporting equipment, before finding more popularity as a mattress filling. Architectural innovation encompasses this "slow spring back foam" technology. Memory foam is the most frequent name for it.
Radical Innovation is when a company applies new technology to a new market. When a new product, technique, or service with significant technological advancement has a large market impact and fully replaces an existing offering, this can also be referred to as disruptive innovation. This is a long-term process of invention.
This happens when new technology and products are developed to serve an existing market. New technology enables this type of innovation by providing a more efficient and accessible alternative to what is already available on the market.
Businesses use disruptive innovation to meet the changing needs of their customers, resulting in the creation of whole new value streams and service offerings that did not exist previously. Disruptive innovation typically begins at the low end of the market sector, but as the technology matures, it eventually supplants existing industry leaders. This type of invention occurs over a medium to a lengthy period of time.

The root of the issue is that, at first, innovation, particularly disruptive innovation, is often inferior to existing products and services on the market when judged against the same metrics and value drivers. As a result, the new items will initially be valuable only to a tiny fraction of the market with distinct value drivers, and will not be of interest to mainstream or high-end customers, where the company generally earns better profit margins.
To put it another way, disruptive innovation initially caters to a limited and unprofitable customer base, which is why established companies with logical decision-making processes typically opt out of disruptive projects in their early stages. When a disruptive innovation enters the mainstream, established organizations frequently pick up on it again, but it's usually too late by then because the new competitor is on the exponential part of the S-curve.

The Three Horizons of Growth, developed by McKinsey & Company, is a prominent approach for assisting companies in structuring their efforts and finding a suitable balance between short and long-term projects in their portfolio. The model's underlying concept is straightforward; in order to optimize a company's growth potential, it must simultaneously work on projects across all three horizons.
You may see solid short-term increases in your numbers if you focus entirely on incrementally improving your existing business with Horizon 1 activities, but you will ultimately forfeit the company's long-term growth. The opposite is true if you focus only on horizon 3 disruptive innovation while completely ignoring your current business. You may have a great future ahead of you, but you may find yourself out of business before you get there. You'll not only optimize your growth potential but also lower the risk of your business portfolio if you strike the appropriate balance.

Disruptive innovation necessitates access to ignored or neglected markets as well as technology that may turn a product into one that is more accessible and inexpensive. The network of partners—suppliers, contractors, and distributors—must profit from the new, disruptive business model in order for it to be disruptive. Certain requirements include:
Enabling technology is described in business as technologies and innovations that significantly modify or improve processes or how people do things. Enabling technology, in the context of disruptive innovation, is the technology or invention that enables the affordability and availability of a product to a larger market. Essentially, the rate at which a market can be disrupted is determined by the rate at which technology is produced and improved. The speed of the disruption, on the other hand, is not always a criterion used to assess the success of the disruption.
The innovative business model is one that employs innovations to reach new or lower-tier clients. These sectors, in general, do not produce earnings for established firms, nor do they purchase their services since they cannot afford them or the items are too complicated for users. This business strategy, which incumbents have not embraced due to the disruptor's initial low-profit margins, tries to deliver simple, cost-effective alternatives.
The upstream and downstream business partners who profit from a successful disruption are included in the coherent value network. To adopt or adhere to the new business model, distributors, suppliers, and vendors may require process adjustments or restructuring. To avoid failure, network members must subscribe to the new business model. Otherwise, by not adhering to the purpose of disruption, existing network processes would have unfavourable effects.
Creating the next disruptive, billion-dollar business idea doesn't happen in the blink of an eye. You need the proper ability to look beyond industry conventions, as well as the correct time to convince others to care about your concept.
To disrupt a market, you must be willing to cannibalize your existing business, be nimble and embrace taking risks. Creating disruptive innovation might be difficult, but that doesn't imply there's nothing you can do to prepare for it — you just have to approach it differently. Here are some ways for you to prepare for disruption:
Being overconfident in your ability to change and dismissing the possibility of others succeeding is a definite way to get caught off guard in the continual process of innovation.
Keeping a watch on new entries in the industry and learning what differentiates them from the established ones is thus something worth paying attention to.
Although these new entrants may be targeting different consumer categories, for the time being, you don't want to miss out on prospective growth chances by focusing solely on what's currently working for your present customer base.
To stay up with the constant change, it's vital to ask the correct questions and keep the consumer at the forefront of your mind so you know exactly what they want and need.
Although technology facilitates a lot and is frequently at the heart of disruptive innovation, you don't necessarily have to employ revolutionary technology to create a shift.
Business model innovation may be used to improve how your organisation offers value to consumers or obtains value from the market.
Disruptive innovation should be approached iteratively and patiently. Market disruption does not occur immediately, and even the most significant changes for development are frequently uncovered through smaller, incremental changes.
As the preceding examples demonstrate, none of the firms was successful from the start, but instead had to go through numerous stages in order to eventually reach the mainstream and maintain their market position.
Moving ahead early and becoming enthused about tiny victories is critical in the process of identifying larger disruptive prospects. You're going to encounter a lot of roadblocks along the way, which is why it's critical not to become disheartened if (or when) things go wrong, but to view your disruptive efforts as learning opportunities.
While patience is essential, you need to also have a clear idea of what is possible and what you want to achieve. Making a detailed plan to lead you in the intended direction is one approach to ensure you're on the correct track.
The key to disruptive innovation is the ability to break the existing operating model and create the right conditions for the emergence of a new one. Disruption is about doing things differently and making a purposeful decision to try to influence the industry's common perceptions. You must generate new types of value and commit to them, even if they are not the most profitable in the short term.